Want to know how does a boiler work? What is a boiler? We’ll explain how different kinds of boilers operate.
How a boiler works really depend on the kind of boiler you have. But the primary purpose of all boilers is to transfer heat to water. Basically, boilers work by heating water or producing steam that is then used to heat a home.
But before that, let’s look more closely at the fundamental definition of a boiler and the general operating procedure that all boilers use.
What is a Boiler?
The boiler is a white metal appliance that is typically found in the kitchen, though it can also be found in other rooms of the house, outside in a garage or outhouse, or in the garden. Since it generates the heat, it is the most crucial component of a central heating system. In essence, it is a tiny furnace that runs on gas, oil, or LPG. In the UK, natural gas, which is automatically fed through from the national gas grid, is the main fuel for boilers. Boiler types vary according to how they function, but we will get into that in more detail later.
The Boiler Process
- The boiler is activated when the thermostat in your house detects a drop in the temperature inside.
- Your boiler starts up and produces heat using either oil, gas, or electricity.
- The boiler’s water is heated using the heat from the fuel source.
- Through radiators or radiant floor systems, heated water or steam is distributed throughout your home, where it radiates heat to warm the air.
- In order to continue heating your home, the water returns to your boiler as it cools (or the steam condenses). There, it is reheated.
- This process continues until your home reaches the desired temperature and your thermostat signals for the boiler to turn off.
Now that you are familiar with the fundamentals of how a boiler works, let’s examine the various types of boilers and how they differ from one another.
Types of Boiler Systems & How They Work
Steam Boiler
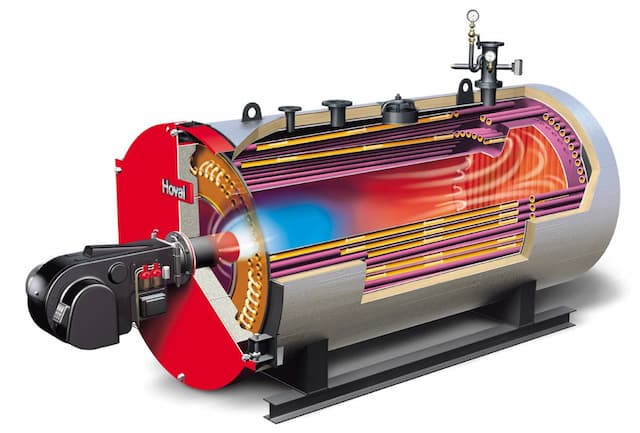
Steam boilers work by electrically igniting the mixture of air and fuel to produce a combustion reaction. This raises the temperature of water-immersed tubes inside the boiler. The water’s temperature is increased by the heat to approximately 212°F, which is the highest temperature at which water can still be liquid at this pressure. Steam is produced as a result, turning the water that the tubes are submerged in into liquid. To provide indoor heating, the steam is piped throughout the building from the boiler to the radiators. As the steam cools down in the radiators and pipes, it turns into liquid water, which then travels through the pipes back to the boiler’s water heating chamber to complete the cycle.
Hot Water Boiler
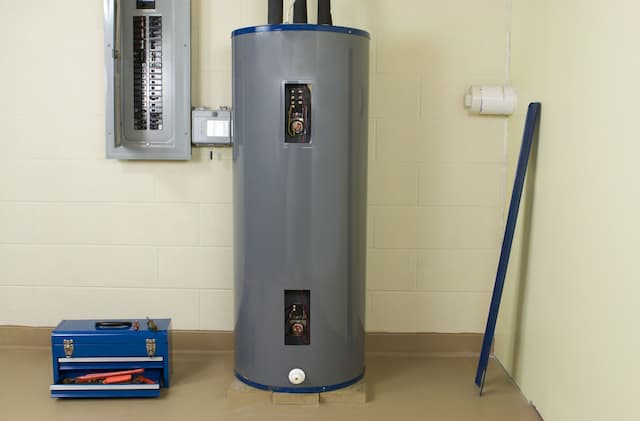

Depending on the type of system, a hot water boiler generates heat energy using either gas or oil fuel. With the help of this energy, the boiler water is heated to a temperature high enough to operate your home’s radiators and heat it.
Gas Boiler
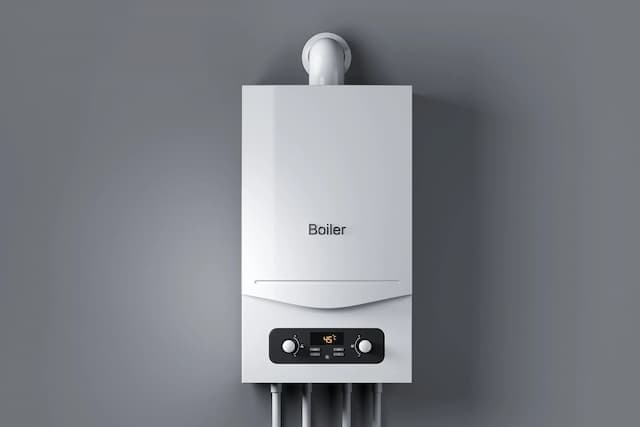

With the help of tiny jets, a gas valve in a gas boiler releases the fuel into a sealed combustion chamber. The gas is ignited electrically to burn, producing heat. An adjacent pipe that carries cold water absorbs this heat. To maintain the heated interior environment you desire, the water is heated to about 180°F and transferred to the radiators throughout your home.
Oil Boiler

Boilers that use oil as fuel operate similarly to those that use gas. By heating water and transferring it through a network of pipes and radiators that disperse heat throughout your house, they maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. The key distinction between them is that these systems use oil combustion as opposed to gas combustion to produce heat.
When the cooled water from heating your home’s radiators returns, an oil burner begins to operate. This cooled water in the boiler lowers the temperature of the boiler water until it activates a temperature sensor, which sets off an electric charge that turns on the oil burner. When the system is activated, it uses high pressure to spray tiny oil droplets into the fire chamber. These minute oil droplets are easily combustible and vaporize into a fine mist. An oil boiler sprays oil droplets that are then ignited by a spark from a high voltage ignition system, sufficiently heating the water that will be used to heat your home.
Summary
So let’s review some of the lessons from this article.
Not just for us on a domestic level, but also at a commercial and industrial level, boilers are a very versatile and significant piece of engineering equipment.
We require a fuel source to produce heat. A reaction can occur when there is a fuel source, heat, and an oxidizing agent present. Thus, the heat source is maintained.
Steam is created at incredibly high pressures to generate enormous amounts of energy by heating water tubes and heating a tank with fire tubes.
We sincerely hope you have enjoyed this brief introduction to boilers.
At RealPars, we have a team of professionals available to respond to your inquiries and concerns. If you have ideas for subjects you’d like our team to cover, please let us know.
Do you know a friend, client, or coworker who could benefit from some of this knowledge? Spread the word about this article.
Happy learning。



